- Our Models
- ServicesHesitant in service?
Get in touch with us with your business problem and we’ll consult you on the suitable service solution.
- SolutionsApplicationsLegacy SupportOther Microsoft SolutionsPower Platform ConsultantsAzure ConsultantsAzure Developers
- Industries
- Our Company
 About Us
About UsLearn more about our HireDynamicsDevelopers portal and the team behind it.
Case StudiesRead successful stories from our clients across various industries.
ServicesFind the right service according to your specific business needs.

- Resources
- Our Models
- ServicesHesitant in service?
Get in touch with us with your business problem and we’ll consult you on the suitable service solution.
- SolutionsApplicationsLegacy SupportOther Microsoft SolutionsPower Platform ConsultantsAzure ConsultantsAzure Developers
- Industries
- Our Company
 About Us
About UsLearn more about our HireDynamicsDevelopers portal and the team behind it.
Case StudiesRead successful stories from our clients across various industries.
ServicesFind the right service according to your specific business needs.

- Resources
Understanding Different Types of Power Apps
Updated: December 18th, 2024 by Ivan Farafonov
Microsoft Power Apps is a powerful platform that enables businesses to build custom applications tailored to their unique needs without requiring extensive coding expertise. By empowering both professional developers and business users, Power Apps helps organizations streamline workflows, automate processes, and enhance productivity.
In this article, we will explore the 3 types of Power Apps:
- Canvas Apps,
- Model-Driven Apps,
- Power Pages.
By understanding their key features, use cases, and best practices, you can make informed decisions about which type of Power App is best for your organization’s needs.
Canvas Apps
Canvas Apps in Power Apps are highly flexible and customizable apps where you start with a blank canvas and design the user interface by dragging and dropping controls like buttons, text boxes, and images. Power Apps developers have full control over the app’s layout and functionality, making it ideal for scenarios where you need to create highly tailored user experiences.
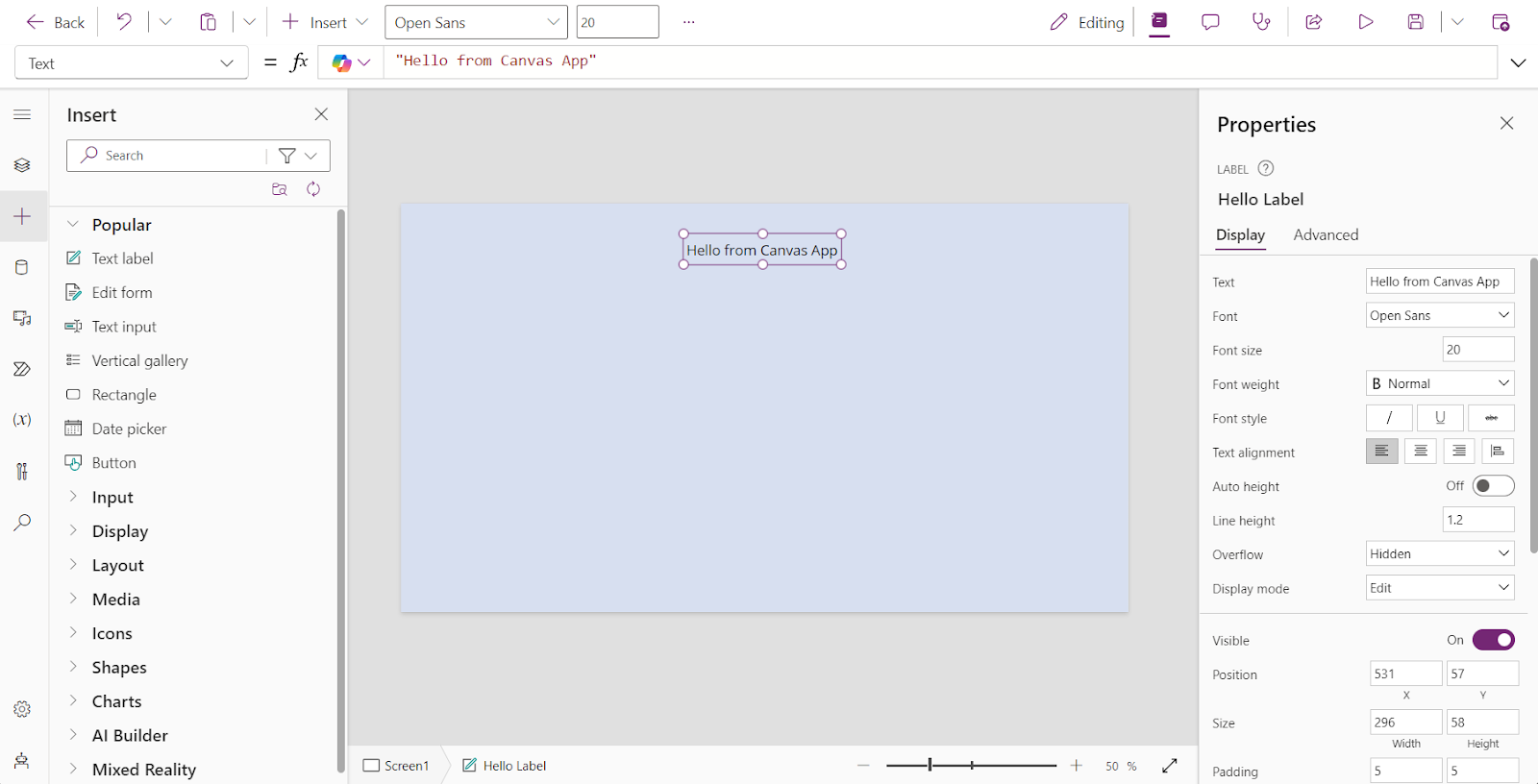
You can start creating your Canvas App using one of the templates provided by Microsoft. Additionally, you can choose whether your app will be optimized for tablets or phones, allowing your application to have a responsive layout based on the devices your users are most likely to use.
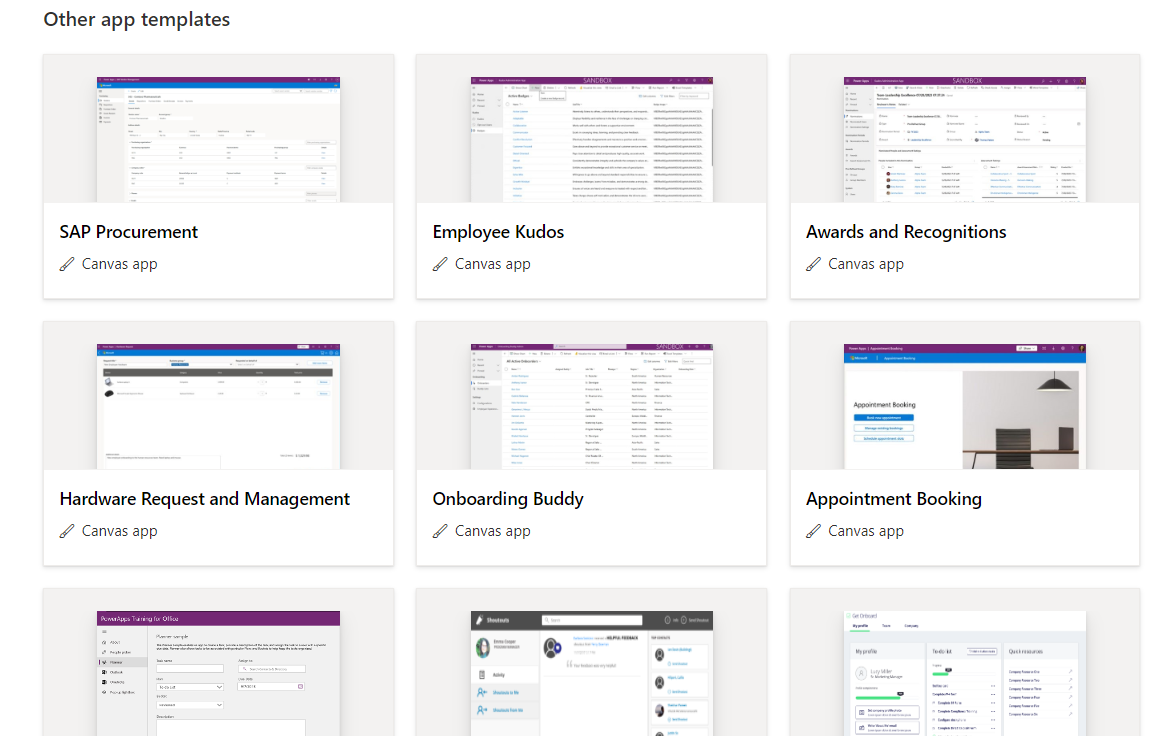
Canvas Apps can connect to a vast range of data sources – over 200 connectors are available – which makes it highly versatile and suitable for many different scenarios. This includes Microsoft-native services and external systems, giving you the power to pull and push data across platforms. Common connectors include SQL Server, Excel, SharePoint, Dynamics 365, Azure, and OneDrive, but the list continues to expand as Microsoft adds more capabilities.
One of the standout features of Canvas Apps is that it allows users to implement custom logic through formulas that resemble Excel expressions. This lowers the barrier for business users or “citizen developers” who are already familiar with spreadsheet functions. These expressions are used to manipulate data, control app behavior, and handle user interactions.
The syntax used in Power Apps formulas is very similar to Excel, making it intuitive. For example, if you want to set the visibility of a button based on a condition, you can use a formula like:
If(IsBlank(TextInput1.Text), false, true)
Best practices for Canvas Apps
- Start with design: Since layout is freeform, planning the design ensures a cleaner interface.
- Keep It Simple: Too many controls or complex formulas can affect app performance, so keep designs minimal and user-friendly.
- Optimize for Mobile and Desktop: Since you control layout, make sure to test your app on both mobile devices and desktops for usability.
Our Power Apps Expert's Opinion
Canvas Apps are ideal when you need complete control over the app’s design and user interface. They provide unmatched flexibility, allowing you to drag-and-drop elements, customize layouts, and design the user experience precisely to fit your business needs. With Canvas Apps, you can integrate multiple data sources such as Microsoft services (like SharePoint and SQL Server) and third-party APIs (like Salesforce and Google Drive).
This makes Canvas Apps perfect for task-specific applications like mobile-friendly field service apps, where workers can update inventory or submit requests in real-time, or expense reporting tools that let employees log and submit expenses with ease. Essentially, if your application requires a highly tailored user interface and integrates with various data sources, Canvas Apps are the way to go.
Hire experts with us to choose and implement Power Apps smoothly!
Model-Driven Apps
Model-driven apps in Power Apps are built on top of Dataverse, which means the structure and data model drive the app design rather than manual control over the user interface. This type of app focuses on complex, data-driven solutions where the business processes and relationships between data entities are paramount. Model-driven apps offer a more standardized layout, with the user experience automatically generated based on the data model you define.
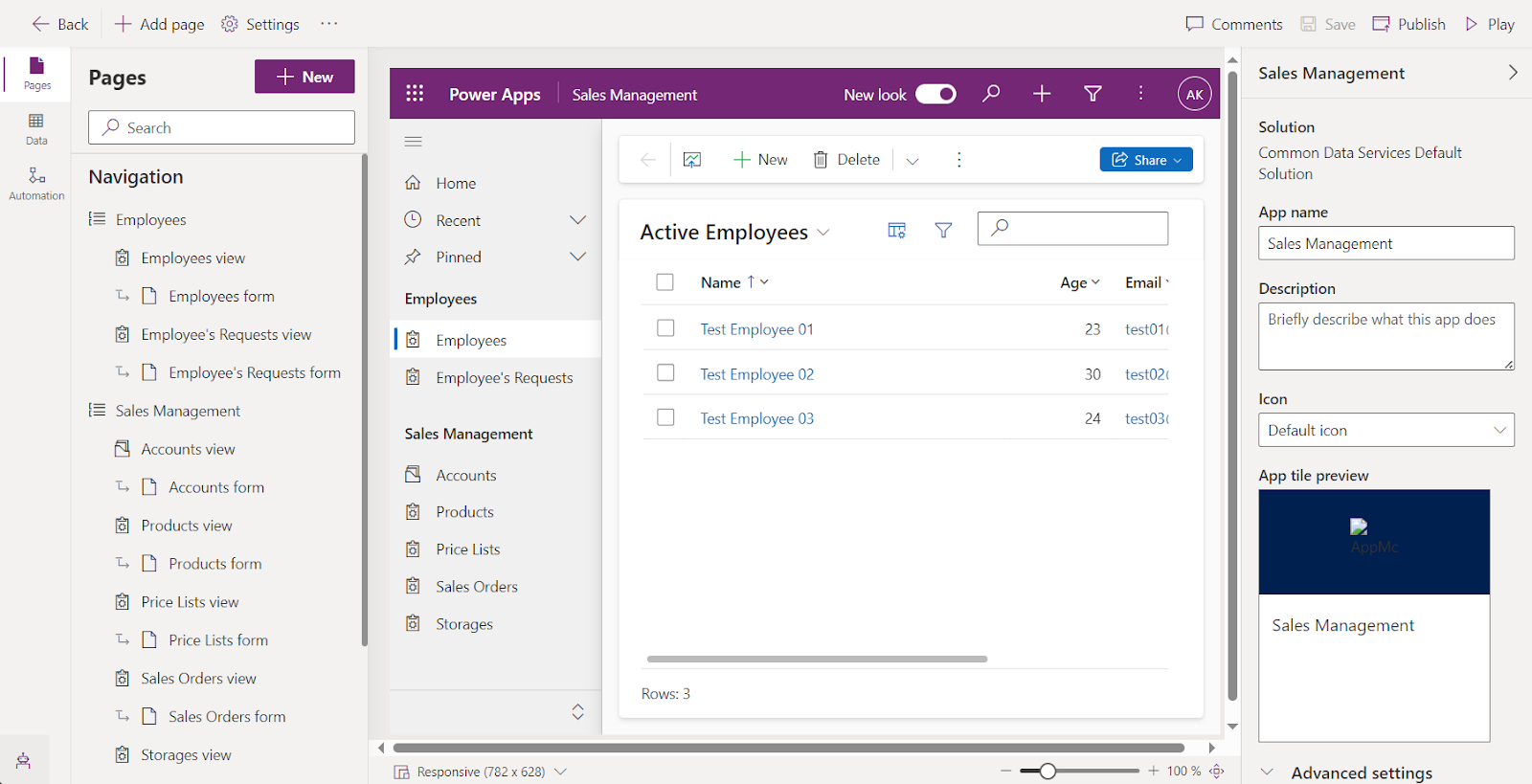
Unlike Canvas Apps, where design flexibility is the main focus, Model-driven apps emphasize data management and relationships between entities. The app’s layout is determined by the data structure (entities, forms, views, charts). The layout is responsive by default, adjusting automatically for different device sizes (desktop, tablet, or mobile), saving developers time in designing different views.
In Model-driven apps, security is a critical component, and it’s managed through Dataverse (the underlying data platform for Power Apps). The platform uses a robust role-based security model, which ensures that users only have access to data that is relevant to their role, minimizing the risk of unauthorized access.
Process automation is one of the most powerful features of Model-driven apps. It allows you to standardize workflows and processes so that users follow a consistent path, ensuring uniformity and reducing human error. One of the primary tools used for this is the Business Process Flow.
Business Process Flows provide a visual guide to users, showing them the steps they need to take to complete a business process (like qualifying a lead or resolving a customer support case).
Model-driven apps can also utilize Workflows and Business Rules for no-code automation of various processes, such as validating user input on forms or sending email notifications when certain actions occur within the system. Additionally, developers can implement more complex logic using custom plug-ins and JavaScript.
Best Practices for Model-driven Apps
- Leverage Dataverse Relationships: Model-driven apps are designed for relational data, so it’s essential to define and maintain entity relationships within Dataverse. This helps in building richer user experiences, especially when users are navigating between related records.
- Role-Based Security: Take advantage of role-based access to control who can view, edit, or delete records, ensuring that sensitive information is only accessible to authorized personnel.
- Automation: Use different tools, like Business Process Flows, Power Automate, and Business Rules to automate processes in your app.
Our Power Apps Expert's Opinion
Model-Driven Apps take a more structured, data-first approach. Instead of focusing on design flexibility, these apps center around data management and automation of business processes. Built on Dataverse, they provide a responsive, auto-generated layout, making them well-suited for more complex applications where data relationships and workflows are critical.
Model-driven apps are excellent for scenarios like CRM systems, where businesses manage customer data, sales leads, and opportunities, or project management solutions that track tasks, milestones, and project timelines. With built-in tools like Business Process Flows and automated workflows, these apps ensure consistency and efficiency, making them perfect for industries requiring robust data management and process automation, such as sales, customer support, or compliance management.
Power Pages
Power Pages (formerly known as Power Apps Portals) is a type of Power App that allows you to create external-facing websites where users outside your organization can interact with data stored in Dataverse. These websites can be used to provide services to customers, partners, or other external stakeholders. Power Pages combine web development with the power of Dataverse to enable businesses to build professional websites for various scenarios, including self-service portals, registration sites, and customer support platforms.
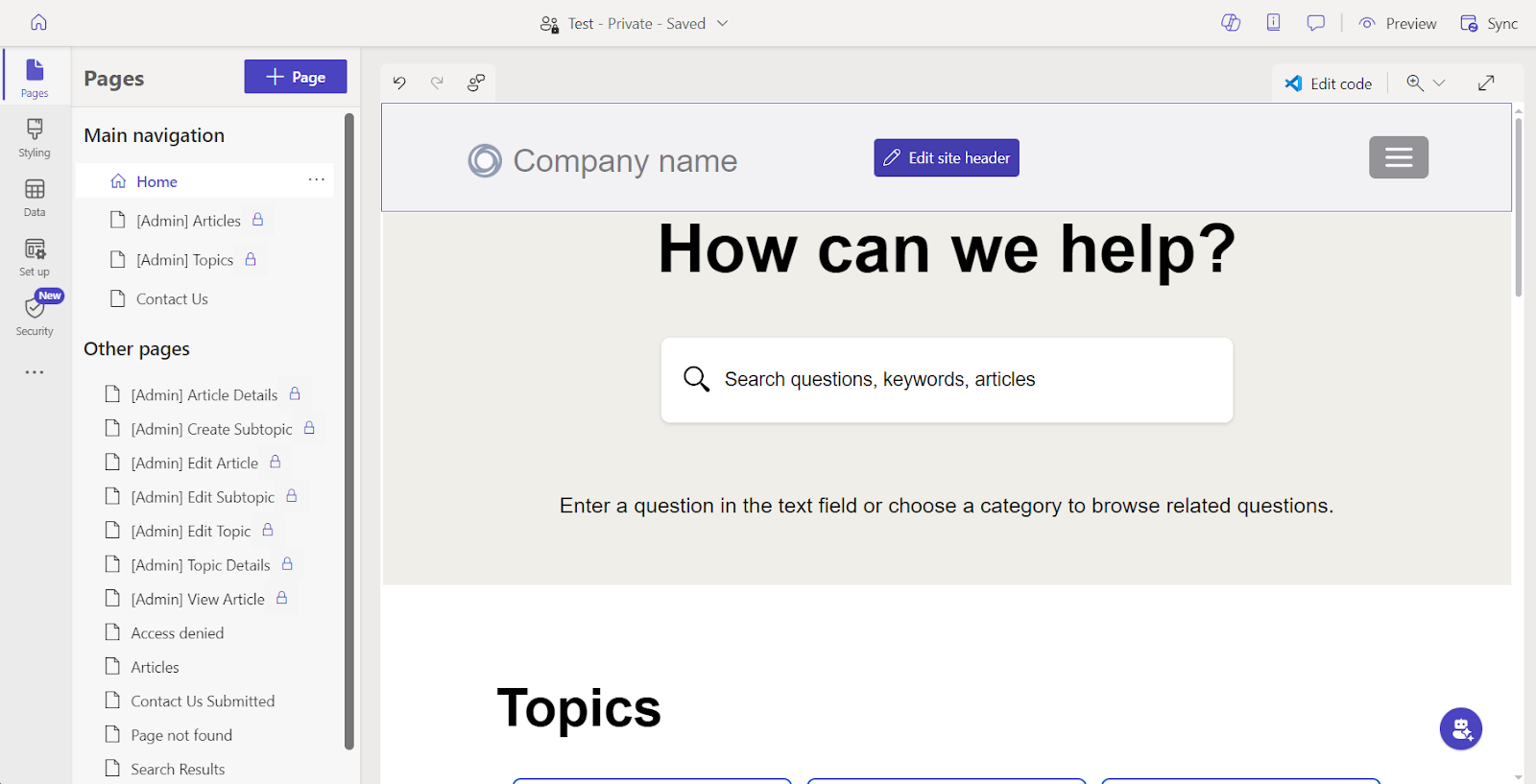
Unlike Canvas or Model-driven apps, Power Pages are designed for both internal and external users. This means you can build portals where people outside your organization can log in, access specific information, and interact with data. Power Pages integrate with Azure Active Directory, Microsoft accounts, and third-party authentication providers (like Google, LinkedIn, and Facebook) to securely manage user logins.
Administrators can create, edit, and manage the web pages, forms, and data views within the portal using the built-in Power Pages Designer. This provides an easy way to control the site content without deep technical skills.
Power Pages can be extended with custom HTML, JavaScript, and CSS to provide more advanced functionality and designs. For developers, the platform also supports integration with Power Automate and other services in the Power Platform.
Best Practices for Power Pages
- User Experience Matters: Since Power Pages are often used by external users, it’s essential to focus on providing an intuitive and seamless user experience. Ensure navigation is straightforward, and forms are easy to fill out, reducing any friction for end-users.
- Secure Data Access: Leverage role-based permissions to control what data users can see or edit. For example, ensure that external users can only access their own records and are restricted from viewing others’ data.
- Optimize for Mobile: Many users will access Power Pages via mobile devices. Ensure that your pages are responsive and mobile-friendly, so they display well on different screen sizes.
- Utilize Power Automate: Integrate workflows to enhance the functionality of Power Pages.
Our Power Apps Expert's Opinion
Power Pages bring a different focus by enabling organizations to create external-facing web portals where users outside the organization—such as customers, partners, or vendors – can interact with Dataverse data. These portals are ideal for building self-service platforms, customer support portals, or vendor management systems, where external users can log in securely, access their data, submit requests, or update records. Power Pages offer secure identity management, including integration with Azure Active Directory and third-party authentication providers like Google and LinkedIn, ensuring external users have controlled access to relevant information.
With customization options through HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, Power Pages can also be adapted to meet specific business needs and designs. For example, you can use Power Pages to create event registration portals, where attendees can sign up, track their participation, and receive event details.
If you need help with the implementation of Power Apps solutions, you may hire Power Apps consultant. Experts provide reliable advice and customize tools to your business needs.
Some of Our Power Apps Experts











Summary
Now that you are familiar with available Power Apps types, let’s summarize the information to better understand which one you need based on the business needs.
When choosing a type of Microsoft Power Apps, the first step is to clearly define your business requirements. If you require a highly customizable user experience, Canvas Apps are the best choice. For structured data management and process automation, Model-Driven Apps excel.
Finally, if your goal is to provide external users with secure, interactive access to your organization’s data, Power Pages are the ideal solution. Each type serves its unique purpose, helping organizations build powerful, user-friendly applications tailored to their specific needs.
Need assistance with Power Apps implementation?
Get in touch with us to hire consultants!
Outline

Mario H.
10 HOURS / WEEK

Alejandro G. T.
30 HOURS / WEEK

Tatyana S.
40 HOURS / WEEK
Request Our Services
Discover Different Types of Power Apps and Choose The Best One!
Your Partner Recognized in Dynamics Community
















